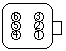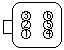|
General Disclaimer: (HV) (DC) injury or death hazard, use at your own risk, may void warranty. |
Escape PHEV TechInfo
Technical information on the Ford Escape useful when designing a Escape PHEV conversion.
Unless otherwise noted, everything refers to a 2007 year model, belonging to [| Hybrids Plus].
Traction battery
Removal
From the hatch opening:
- Remove the carpet in the hatch compartment floor, to reveal the battery
- Turn the orange safety plug from LOCK to UNLOCK and pull it out
- Remove the black plastic air coupling on the rear-left
- Remove the bolts on either side of the battery (3 bolts on each side)
- Disconnect the battery:
- Orange HV connector on the right (flip the lever)
- Big black signal connector on the left (unscrews)
- Small connector next to the signal connector (snaps)
- Hook an engine hoist to the two round holes in the black metal on either side of the battery
- Hoist the battery out of the car
To open the battery:
- You need a #35 security Torx driver, and a #35 Torx driver
- Remove all the screws in the 2 top covers
- Cover over the fans
- Cover over the batteries and electronics
Component locations
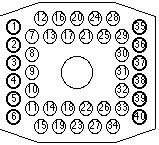
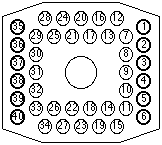
The battery includes (as seen when in the vehicle):
- Air blowers in the rear compartment
- NiMH cells in the center
- 2 layers of cells
- each layer in a left and right group
- each group has 13 columns of 5 cells in series
- total: 2 * 2 * 13 * 5 = 260 cells
- pack voltage: 1.3 V * 260 = 338 V
- controller on the right side
- contactors and HV connector on the right-front corner
- safety plug on the left-right corner
- the Converter on the left side
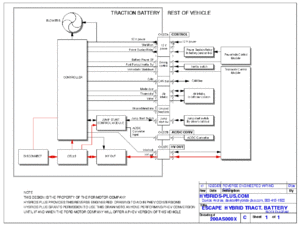
Block diagram
This block diagram shows the main components of the battery pack, and how they interface to the vehicle
- The NiMH cells store energy
- The battery controller controls the battery pack
- It communicates with the vehicle through the CAN bus
- It monitors the air intake temperature, it controls the intake air flow and source, and it drives to DC blowers to blow air into the cells
- It monitors the cells' voltage, including in intermediate points of the pack ("taps")
- ...
- The DC-DC converter receives power from the 12 V battery and boosts it up to 300 V, to charge the traction battery when it's dead and the user presses the Jump Start button (by the driver's left foot)
- The Safety Disconnects opens the pack mid-voltage
- The HV Output section
- It has a connector with 2 high-current contacts to connect the battery voltage to the vehicle
- It has a pair of wires to determine if that connector is connected or not
- It has contactors (high power relays) to connect or isolate the pack voltage
- The blower compartment has 2 DC blowers to blow air into the cells
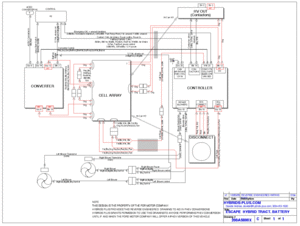
Wiring diagram
This wiring diagram shows how the components of the battery pack are wired together.
- High voltage wires are red.
- Connectors are marked with their color and the number of positions
- Sets of wires are shown together. The slash at one end indicates the number of wires
- The function of sets of wires is shown above the wire
- The wire colors are shown below the set of wires
- Shaded squares indicate that wires are bundled together
- The orientation of the components is shown as seen when looking from the hatch
This reverse engineering drawing is not guaranteed to be accurate and is offered as-is. Please direct corrections to DavideAndrea.
Connectors
The battery has 3 connectors, with a total of 34 wires:
- C4227A - 28 wires - control
- C4227B - 2 wires - low power HV to the AC/DC converter
- C4227C - 4 wires - traction HV, interlock signals
AC/DC converter connector: C4227B
The AC/DC converter connector has 2 circuits, with the following names and functions.
| Group | Ckt | Pin(s) | Ext. color | Int. color | Name | Function | Notes |
| AC/DC converter in | 3000 | 1 | Vio | Red | AC/DC in+ | ??? | |
| 3001 | 1 | VioOrg | Blk | AC/DC in- |
Control connector: C4227A
The big control connector has 24 circuits, with the following names and functions.
| Group | Ckt | Pin(s) | Ext. color | Int. color | Name | Function | Notes |
| 12V pwr | 57 | 35,36,37 | LtgrnBlk | Blk | Ground | Power ground | |
| 570 | 30,31 | BlkWht | BlkWht | Ground | Signal ground | ||
| 3800 | 4,5,6 | LtgrnBlk | Red | +12 V | Power +12V | Always on | |
| 16 | 10,11 | +12 V | RedLtgrn | RedBlu | Low power +12V | Always on | |
| 3206 | 19 | LtgrnYel | TanRed | Voltage supplied in Start and Run | Receives 12 V when the car is on | From the ignition switch. Overload protected | |
| 3997 | 14 | Dkgrn | Tan | Power sustain relay out | Receives 12 V when the Powertrain Control Module's Power Relay is on | The relay is located in the Battery Junction Box. The Powertrain Control Module is located under the hood, in the rear-center | |
| Air intake | 3703 | 21 | BrnWht | BlkBrn | Battery compartment thermistor signal | Senses air intake temperature | All are located inside the column at the rear-left corner of car, inside air intake ducts |
| 3704 | 25 | DkgrnWht | WhtBlk | Battery compartment thermistor return | |||
| 698 | 34 | Red | RedBlu | Mode door actuator motor + | Moves a flap controlling air flow | ||
| 699 | 26 | Org | BlkYel | Mode door actuator motor - | |||
| 1129 | 17 | BrnWht | RedGRn | Mode door actuator potentiometer + | Senses position of flap | ||
| 1130 | 20 | PnkLtgrn | BluBlk | Mode door actuator potentiometer wiper | |||
| 1128 | 24 | GryLtBlu | BlkWht | Mode door actuator potentiometer - | |||
| 698 | 34 | Red | RedBlu | Zone Valve | Solenoid selecting air source | ||
| CAN BUS | 1908 | 29 | Wht | YelRed | High speed CAN bus + | Communicates with vehicle | See CAN section below for messages |
| 1909 | 28 | Blk | YelWht | High speed CAN bus - | |||
| Jump start switch | 176 | 16 | PnkLtgrn | BrnWht | Jump start switch feed | When grounded, lets 12 V battery jump charge-up the traction battery a bit, through DC-DC converter in battery pack, enough to start the car | The switch is located to the left of the driver's left ankle, behind a black plastic panel |
| 179 | 12 | OrgRed | GrnBlk | Jump start switch illumination + | When at 12 V, it lights-up the switch
| ||
| Emergency control | 3003 | 8 | VioWht | Tan | Battery power off signal | ??? | The Power Train Control Module is located under the hood, in the rear-center |
| 877 | 7,23 | Wht | RedBlk | Fuel pump feed / Inertia Sw input | Normally at +12V; open in case a crash opens an inertia switch | The High Voltage Cutoff switch is located in the right-rear column of the car | |
| 212 | 27 | Dkblu | BlkBlu | Immediate shutdown 1 | The Transaxle Control Module tells the battery to remove power to the vehicle? | The Transaxle Control Module is under the hood, in the center, to the left of the box labeled "HYBRID" | |
| 213 | 13 | DkbluYel | BlkRed | Immediate shutdown 2 | |||
| Unused | n.a. | 18 | n.a. | TanRed | ??? | ??? | Connected to controller, not used in vehicle |
| 32 | YelBlk |
HV connector: C4227C
The HV connector has 4 circuits, with the following names and functions.
| Group | Ckt | Pin(s) | Ext. color | Int. color | Name | Function | Notes |
| HV | 3180 | + | Org | n.a. | HV+ | Battery power | To Transaxle Control Module |
| 3181 | - | Org | HV- | ||||
| Interlock | 3130 | 1 | Gry | Wht or Blu | Traction Battery Control Module Interlock + | Detects if HV connector is mated | To Transaxle Control Module |
| 3181 | 2 | Red | Blu or Wht | Traction Battery Control Module Interlock - |
CAN bus messages
- Kvaser has a simple explanation of the CAN bus.
- wikipedia article on the CAN bus
| General Disclaimer: (HV) (DC) injury or death hazard, use at your own risk, may void warranty. |
|---|
|
HV (High Voltage) DC (Direct Current) Warning: Traction Battery Packs, Motors, Chargers, and other HV sources could cause serious injury or death if proper precautions are not taken while working on or around such High Voltage Direct Current sources. Use this information at your own risk: There is no warranty expressed nor implied and we are not liable for any of your past, present, nor future actions. Even should you perform these modifications to the letter you could still damage any number of components in your vehicle causing it to no longer function. Even if it appears to function properly your actions may cause it to self destruct with collateral damage to surrounding properties other than your vehicle. By utilizing these ideas and instructions in an attempting to enhance national security, reduce gas consumption, vehicle "emissions", your carbon footprint, or smog, you do so at your own risk & peril. Warranty: In performing some of these modifications you may void your warranty with the vehicles manufacturer. See also our My wiki:General disclaimer |